A home inspection report is a comprehensive evaluation of a property’s condition. It serves as a critical tool for homebuyers, owners, and even tenants to understand the state of the property.
The insights provided in the report allow you to identify potential risks, plan maintenance, and negotiate better deals when buying or selling.
For Indian homeowners, where factors like climate, construction quality, and rapid urbanization affect properties significantly.
Understanding this report is essential. Let’s break down the components of a home inspection report and offer a guide to interpreting its findings.
What is a Home Inspection Report?
 A home inspection report is a professional document created after a thorough assessment of a property. It outlines the current condition of various structural and functional aspects of the home.
A home inspection report is a professional document created after a thorough assessment of a property. It outlines the current condition of various structural and functional aspects of the home.
The report includes observations, risk ratings, and recommendations, offering a clear roadmap for repairs or maintenance.
In India, home inspection reports have become increasingly relevant due to varied construction quality and climate-induced issues like dampness and seepage.
By reviewing this report, buyers can make informed decisions and negotiate repairs or costs before finalizing the deal.
Benefits of a Home Inspection Report
Transparency: Provides a clear picture of the property’s condition, ensuring no hidden surprises post-purchase.
Cost Savings: Identifies issues early, saving on expensive repairs down the line.
Safety Assurance: Highlights safety risks, such as faulty wiring or structural weaknesses.
Decision-Making: Empowers buyers to make informed choices, ensuring their investment is worthwhile.
Understanding Key Components of a Home Inspection Report
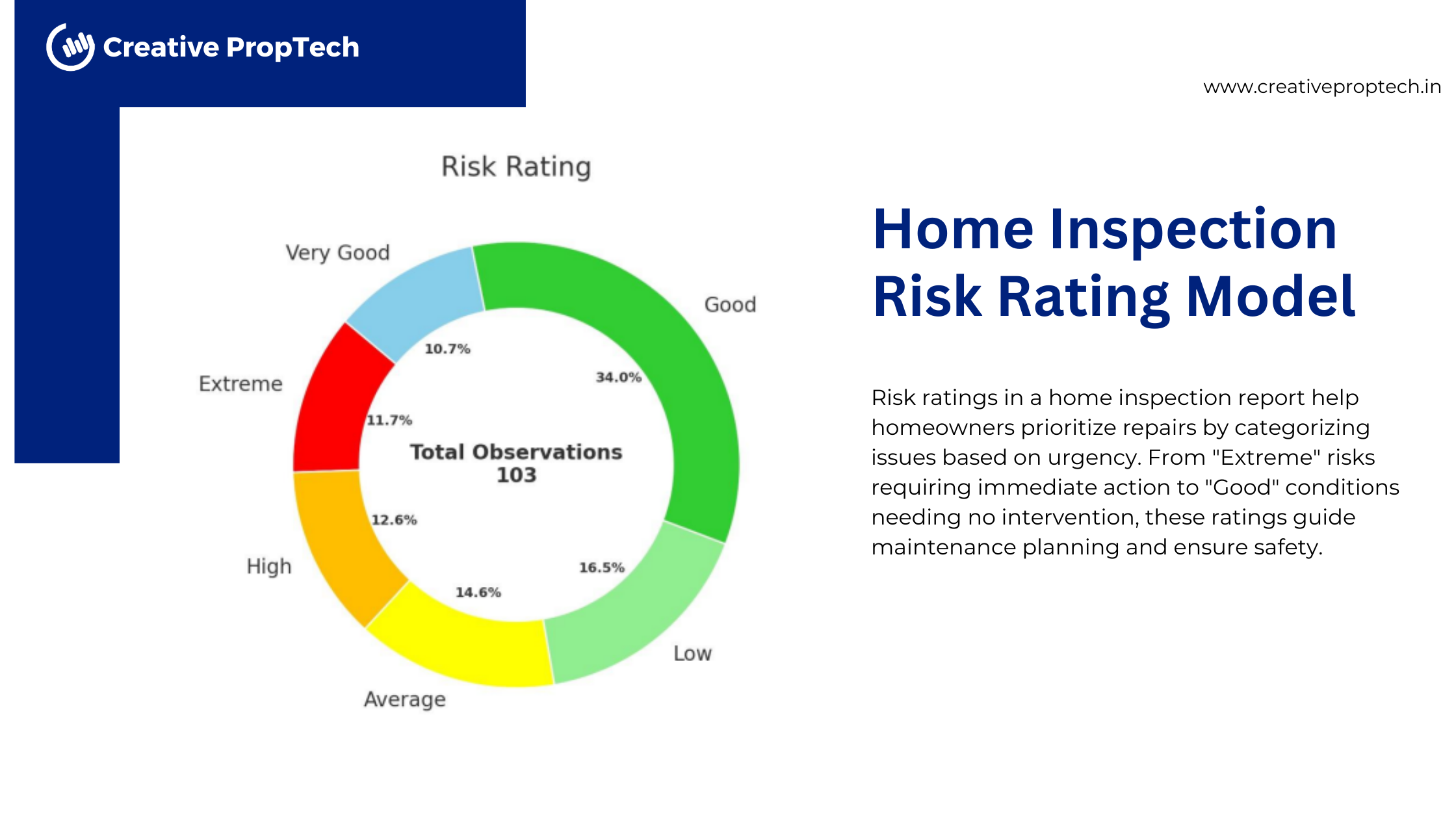
Risk Rating Model
Extreme – These are the risks that are extremely sensitive, that cause substantial harm and
can be hazardous, that requires an immediate action for corrective measures.
High – These are the risks that are not potentially extreme butstill possess functionality
issues and can lead to an undesirable scenario.
Average – These are the risks that are not concerning now, not impacting the Safety or
Functionality, but with time can be damaging and harmful. these can be avoided by
beforehand corrective measures.
Low – These are the risks that are highly un-disruptive and does not possess concerning
behavior until well managed.
Good – Risks in this category are favorable and pose minimal danger. They offer
manageable levels of uncertainty with potentially beneficial outcomes. Good risks are
considered safe and usually represent opportunities rather than threats.
Very Good – This category represents risks that are highly unlikely to result in negative
outcomes and may even offer positive results if managed well. The probability of
occurrence is very low, and if it does materialize, it may lead to positive or neutral
consequences. These risks usually do not need active management beyond regular
periodic review.
Executive Summary
The executive summary provides an overview of the property’s overall condition. It highlights major findings, such as structural cracks, water seepage, or electrical system efficiency, giving a snapshot of key concerns and positive attributes.
Section-wise Breakdown of a Home Inspection Report
The report is divided into sections, each focusing on a specific area of the property:
- Doors: Evaluates the physical condition, alignment, and functionality of doors, including locks and frames.
- Windows: Assesses window frames, glass panes, and mechanisms for damage or operational issues.
- Flooring: Inspects for hollowness, cracks, and leveling issues in floor and wall tiles.
- Walls and Paint: Identifies cracks, dampness, and uneven finishes in interior and exterior walls.
- Ceiling: Examines for structural integrity, cracks, and water damage.
- Electrical Systems: Checks sockets, switches, and voltage stability for proper functioning and safety.
- Plumbing: Reviews fixtures, water pressure, and potential leaks.
- Thermal Inspection: Detects hidden issues like insulation deficiencies, moisture ingress, and electrical hotspots using thermal imaging.
- Aqua Check: Analyzes water quality for pH levels, salinity, and pressure.
Observations and Recommendations
Each section includes detailed observations, risk ratings, and tailored recommendations. This ensures homeowners know the exact issue and the corrective measures needed.
Key Features of the Home Inspection Report
Task Summaries
Each section of a home inspection report begins with a task summary, which outlines the specific methods and tools used to evaluate different aspects of the property. These summaries provide clarity on how the inspection was conducted and what techniques were employed to uncover potential issues. Here’s an expanded list of task summaries commonly found in home inspection reports:
1. Doors
- Inspection Tools: Level spirit, torch, and visual techniques.
- Tasks: Check alignment, smooth operation, and condition of locks and hinges. Assess gaps between the door frame and surrounding walls.
2. Thermal Imaging
 Inspection Tools: Thermal imaging cameras.
Inspection Tools: Thermal imaging cameras.
Tasks: Detect temperature variations to uncover hidden issues such as leaks, insulation gaps, or overheating electrical components.
3. Plumbing Systems
 Inspection Tools: Pressure gauges, moisture meters, and visual inspection.
Inspection Tools: Pressure gauges, moisture meters, and visual inspection.
Tasks: Evaluate water pressure, detect leaks, and inspect the drainage system for proper flow and clogging issues.
4. Electrical Systems
 Inspection Tools: Multimeter, circuit testers, and thermal cameras.
Inspection Tools: Multimeter, circuit testers, and thermal cameras.
Tasks: Test all sockets and switches for functionality, check wiring for wear and tear, and identify electrical hotspots or overheating components.
5. Flooring
 Inspection Tools: Soft-faced hammer, laser level, and visual techniques.
Inspection Tools: Soft-faced hammer, laser level, and visual techniques.
Tasks: Inspect for hollow tiles, uneven surfaces, and signs of cracks or wear.
6. Walls and Paint
 Inspection Tools: Moisture meters, torchlight, and visual inspection.
Inspection Tools: Moisture meters, torchlight, and visual inspection.
Tasks: Assess cracks, dampness, uneven finishes, and peeling paint on interior and exterior walls.
7. Ceilings
 Inspection Tools: Moisture meters, visual inspection, and thermal cameras.
Inspection Tools: Moisture meters, visual inspection, and thermal cameras.
Tasks: Examine for sagging, water stains, and structural cracks.
8. Windows
 Inspection Tools: Torchlight, level spirit, and manual operation tests.
Inspection Tools: Torchlight, level spirit, and manual operation tests.
Tasks: Inspect for smooth opening and closing, check for gaps in seals, and ensure proper alignment.
Observations
The report provides specific observations for each area inspected. Examples include:
- Cracks in walls or gaps in door frames.
- Hollowness in tiles detected with a soft-faced hammer.
- Leaky faucets or improper caulking in plumbing systems.
Recommendations
For every observation, the report includes actionable recommendations. For example:
- Seal cracks with plaster filler for wall issues.
- Use epoxy adhesive for repairing hollow tiles.
- Replace or tighten loose door handles to improve functionality.
Visual Evidence
Photos and thermal images accompany observations, offering visual proof of issues like dampness, seepage, or structural wear.
Interpreting the Risk Ratings of Home Inspection Report
Risk ratings are a vital part of the report, helping homeowners prioritize repairs. Here’s how to interpret them:
- Extreme & High: Immediate attention is required. These include significant structural issues or severe water seepage.
- Average: Plan for maintenance soon to prevent the issue from escalating.
- Low: Minor concerns that can be addressed during routine maintenance.
- Good & Very Good: No immediate action is required; these areas are in excellent condition.
Tips for Using a Home Inspection Report Effectively
a) Read the Executive Summary First
The executive summary is the most concise section of the report, offering a quick snapshot of the property’s overall condition. It highlights the most critical findings, major defects, and high-priority areas that need attention.
b) Prioritize Based on Risk Ratings
The risk rating model in a home inspection report categorizes issues by severity—Extreme, High, Average, Low, and Good. Focusing on high-risk areas ensures that critical issues are addressed promptly, preventing further damage or costly repairs.
c) Verify Recommendations
The report provides recommendations for each issue, but it’s essential to cross-check these suggestions with professionals like contractors, plumbers, or electricians.
d) Use for Future Maintenance
A home inspection report isn’t just for immediate repairs—it’s also a valuable reference document for ongoing maintenance.